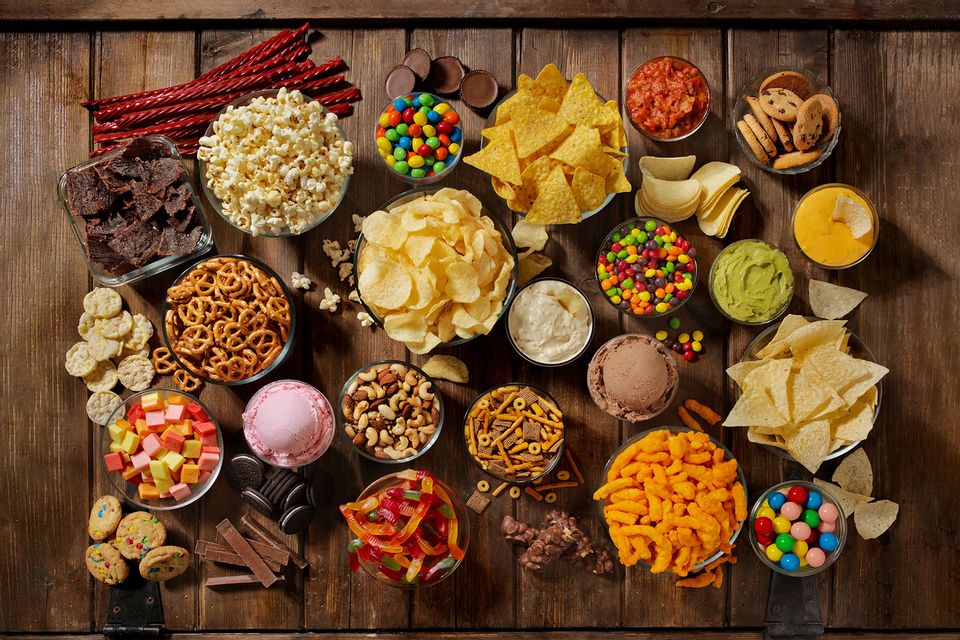
Food plays a central role in our lives, not only as a source of nourishment but also as a source of pleasure and comfort. However, certain foods have been found to trigger addictive responses in the brain, leading to cravings, loss of control, and overconsumption. In contrast, there are foods that are less likely to elicit addictive behaviors and are often associated with health benefits. Understanding the characteristics of these foods can help individuals make informed choices about their diets and overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the 18 most addictive foods and the 17 least addictive ones, along with explanations of why they may have different effects on our brains and bodies.
Understanding Food Addiction
Food addiction is a complex phenomenon involving both psychological and physiological factors. Certain foods, particularly those high in sugar, fat, and salt, can hijack the brain’s reward system, leading to compulsive overeating behaviors similar to those seen in drug addiction. When we consume these foods, they trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, repeated exposure to these highly palatable foods can lead to tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
The 18 Most Addictive Foods
Pizza
Combines high-fat cheese, salty processed meats, and refined carbohydrates in a highly palatable package.
Chocolate
Contains sugar, fat, and caffeine, all of which can stimulate the brain’s reward pathways.
Potato Chips
Crispy, salty, and often high in fat, potato chips can be difficult to stop eating once you start.
Cookies
Sweet, chewy, and often packed with sugar and fat, cookies are a common indulgence.
Ice Cream
Creamy, sweet, and available in countless flavors, ice cream is a classic comfort food.
French Fries
Deep-fried and salty, French fries provide a satisfying crunch and are often difficult to resist.
Cheeseburgers
Offer a combination of protein, fat, and salt, along with the umami flavor of cheese and meat.
Soda (Soft Drinks)
High in sugar or artificial sweeteners, soda provides a quick energy boost and can be habit-forming.
Cake
Sweet, moist, and often frosted, cake is a staple at celebrations and events.
Cheese
Contains casein, a protein that releases casomorphins during digestion, leading to feelings of pleasure and satisfaction.
Bacon
Rich in fat and salt, bacon has a unique flavor profile that many find irresistible.
Fried Chicken
Crispy on the outside and juicy on the inside, fried chicken is a popular comfort food.
Donuts
Sweet, fried, and often glazed or filled, donuts are a decadent treat.
Breakfast Cereal
Often high in sugar and refined carbohydrates, breakfast cereal can be addictive, especially for children.
Chocolate Bars
Combines the addictive properties of chocolate with additional sugar and fat.
Pastries
Whether filled with cream, fruit, or chocolate, pastries are a source of comfort and pleasure for many.
Gummy Candy
Chewy, colorful, and packed with sugar, gummy candy is popular among both children and adults.
Fast Food Burgers
High in fat, salt, and often sugar, fast food burgers are designed to be crave-worthy.
The 17 Least Addictive Foods
Cucumbers
Low in calories and high in water content, cucumbers are refreshing and hydrating.
Carrots
Crunchy, sweet, and packed with nutrients, carrots are a satisfying snack.
Apples
Naturally sweet and high in fiber, apples provide a healthy source of energy.
Broccoli
Nutrient-dense and low in calories, broccoli is a versatile vegetable that can be enjoyed in many ways.
Salmon
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein, salmon is a heart-healthy source of nutrition.
Eggs
High in protein and essential nutrients, eggs are a versatile and filling food.
Oats
High in fiber and complex carbohydrates, oats provide sustained energy and promote satiety.
Quinoa
A complete protein and gluten-free grain, quinoa is a nutritious addition to any meal.
Spinach
Packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, spinach is a nutrient powerhouse.
Almonds
Rich in healthy fats, protein, and fiber, almonds make a satisfying and nutritious snack.
Brown Rice
A whole grain rich in fiber and nutrients, brown rice is a healthy staple in many cuisines.
Bananas
Naturally sweet and portable, bananas are a convenient source of energy.
Plain Yogurt
High in protein and probiotics, plain yogurt is a versatile ingredient in both sweet and savory dishes.
Chicken Breast
Lean and protein-rich, chicken breast is a staple in many healthy diets.
Sweet Potatoes
Packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, sweet potatoes are a nutritious and versatile root vegetable.
Beans
High in fiber and protein, beans are a plant-based source of nutrition that can be incorporated into many dishes.
Watermelon
Juicy, refreshing, and low in calories, watermelon is a hydrating summer treat.
Why Some Foods Are More Addictive Than Others
Several factors contribute to the addictive nature of certain foods
- Sugar, Fat, and Salt Foods high in these ingredients tend to be more palatable and rewarding to the brain.
- Food Processing Highly processed foods often contain additives and flavor enhancers that can increase their addictive potential.
- Texture and Mouthfeel Foods that are crunchy, creamy, or chewy can provide sensory satisfaction that contributes to their addictive nature.
- Marketing and Availability Food companies use marketing strategies to promote their products and make them more appealing and accessible to consumers.
Strategies for Managing Cravings
- Be Mindful: Pay attention to hunger cues and eat slowly to savor the flavors of your food.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and reduce cravings.
- Eat Balanced Meals: Include a combination of protein, healthy fats, and fiber in your meals to promote satiety.
- Plan Ahead: Stock your kitchen with healthy snacks and meals to avoid impulsive choices.
- Practice Moderation: Allow yourself to enjoy your favorite foods occasionally, but in smaller portions.
- Seek Support: Reach out to friends, family, or a professional for support if you’re struggling with food cravings or addiction.
FAQs
Can you really be addicted to food?
Yes, food addiction is a recognized condition characterized by compulsive overeating, cravings, and loss of control around certain foods.
Why are some foods more addictive than others?
Foods high in sugar, fat, and salt can stimulate the brain’s reward system, leading to feelings of pleasure and cravings for more.
Is it possible to overcome food addiction?
Yes, with the help of therapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes, many people are able to overcome food addiction and develop healthier eating habits.
Are there healthier alternatives to addictive foods?
Yes, whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains are less likely to trigger addictive responses in the brain and offer numerous health benefits.
Can food addiction lead to weight gain and other health problems?
Yes, overconsumption of addictive foods can contribute to weight gain, obesity, and various health issues, including diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Should I avoid all addictive foods completely?
While it’s important to limit consumption of highly addictive foods, complete avoidance may not be necessary or practical. Moderation and balance are key to maintaining a healthy relationship with food.
How can I tell if I’m addicted to a certain food?
Signs of food addiction may include preoccupation with food, loss of control over eating, and continued consumption despite negative consequences. If you’re concerned about your eating habits, consider seeking help from a healthcare professional.
By understanding the addictive properties of certain foods and implementing strategies to manage cravings, individuals can take control of their eating habits and make choices that support their overall health and well-being. Incorporating more whole, nutrient-dense foods into your diet and practicing mindful eating can help you break free from the cycle of food addiction and enjoy a balanced and fulfilling relationship with food.